With the increasingly serious problem of "white pollution", traditional plastic disposable tableware is restricted by many countries around the world because it is difficult to degrade.In this context, Biodegradable Disposable Tableware has risen rapidly as an environmentally friendly alternative. This type of product is mainly made of bio-based materials such as polylactic acid (PLA), starch, sugarcane pulp, and bamboo pulp. In the natural environment, it can be decomposed into water, carbon dioxide, and organic matter through microbial action, having a minimal impact on the environment.
?
?
What types of biodegradable materials are used in disposable tableware?
Plant fibers: Materials such as bamboo fiber, wheat straw and reed pulp belong to plant fibers. They are derived from agricultural by-products, have natural degradable characteristics, and can make comprehensive use of agricultural resources. For instance, disposable tableware made from wheat straw can be decomposed into harmless substances by microorganisms in the natural environment after use.
?
PLA (polylactic Acid) : It is produced from starches such as corn and cassava through fermentation processes to produce lactic acid, which is then polymerized. Under industrial composting conditions, it can be completely decomposed within 180 days.Many environmental protection disposable PLA tableware, is made of polylactic acid, both environmental protection and health.
?
PBAT/PBS bio-based plastics: PBAT is polyadipic acid/butylene terephthalate ester, PBS is polybutylene succinate ester.These materials have good ductility and heat resistance, which can meet the needs of disposable tableware in different use scenarios.For example, some high-quality disposable lunch boxes may be made of PBAT materials.
?
Starch: It is mainly made of degradable materials such as starch, which is a renewable natural polymer material with good biodegradability and compatibility.Like the common starch degradable round bowl, it can be decomposed by microorganisms in the natural environment after use, and will not cause pollution to the environment.
?
In addition, PHA (polyhydroxyalkanoates), poly ε -caprolactone (PCL), etc. are also used in the production of disposable tableware.For example, PHA can be used to make disposable tableware, non-woven fabrics, packaging materials and other degradable products;PCL can be completely decomposed by microorganisms in both anaerobic and aerobic environments, and the synthesis process is simple, low cost, and excellent processing performance.
?
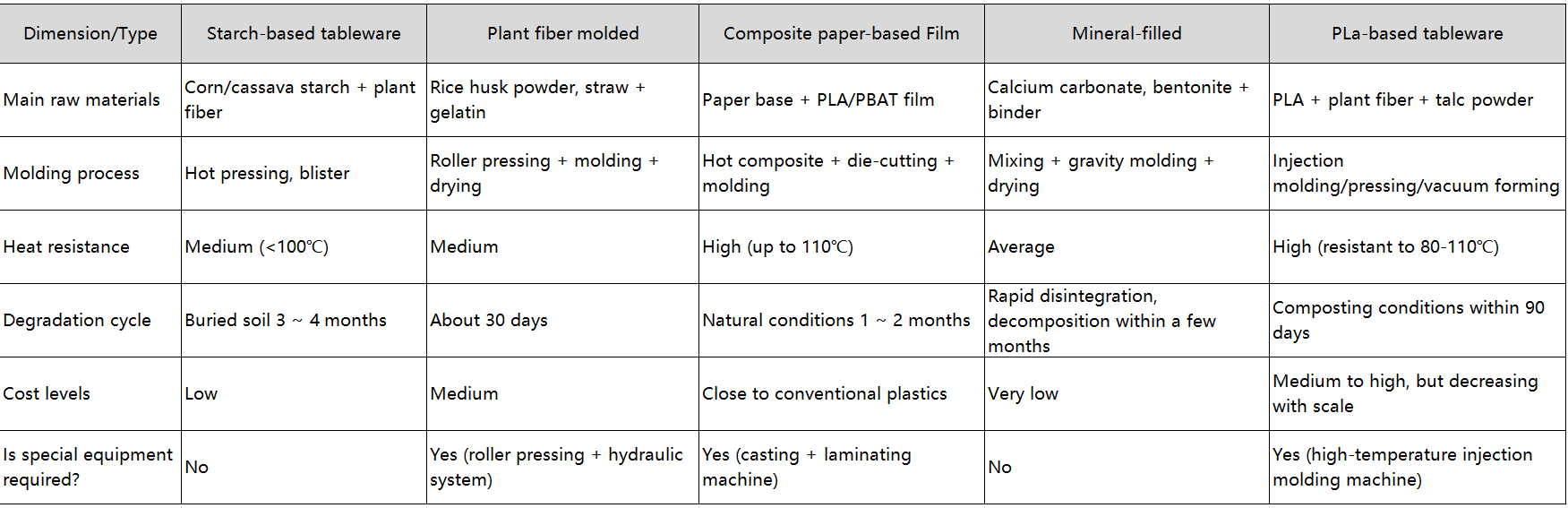
Comparison of main materials and types
?
How are biodegradable disposable tableware made?
With the growing problem of "white pollution", many countries around the world have banned or restricted the use of disposable foam plastic tableware.In order to solve the contradiction between environmental protection and practicality, scientific research institutions and enterprises have developed a variety of disposable tableware production technologies based on natural polymers or biodegradable polymers, with the goal of achieving full life cycle degradation under the premise of ensuring hygiene, strength and cost control.
?
1. Starch-based hot pressing molding method (such as corn starch
This method uses edible starches (such as corn and cassava) as the main raw materials. After adding plasticizers and fillers, tableware is made through mixing, sheeting and hot pressing.
?
Representative patent: A production process of corn starch-based biodegradable disposable tableware.
?
Advantages: The raw materials are renewable and degrade quickly (they can be completely degraded within 3 to 4 months when buried in normal temperature soil). There is no discharge of "three wastes" during the production process.
Disadvantages: Water resistance and mechanical strength depend on additive optimization.
?
2. Plant fiber molding method (such as bamboo powder, rice husk powder)
Using bamboo powder, rice husk powder, bagasse and other plant fibers as the main ingredients, combined with protein gelatin, polyhydroxybutyrate and other adhesives, through crushing, stirring, rolling, setting and other steps.
?
Representative case: Fully biodegradable disposable tableware uses a system of rice husk powder and protein gelatin.
?
Advantages: The waste can be used for composting or as feed, and has high comprehensive utilization value of resources.
Disadvantages: It has high requirements for the pretreatment of raw materials and the anti-mold performance needs to be specially designed.
?
3. PLA film composite paper-based method (polylactic acid technology)
The paper base is used as the support structure, and the surface is composite with a layer of biodegradable film (such as PLA/PBAT blend material), which is completed by flow extrusion, hot pressing and die cutting.
?
Representative solution: A manufacturing method for fully biodegradable disposable tableware.
?
Advantages: It combines the stiffness of paper and the water resistance of PLA, with a heat resistance of up to 110℃, approaching the performance of traditional plastics.
Disadvantage: The price of PLA raw materials is relatively high, but the unit cost can be reduced through large-scale production.
?
4. Inorganic mineral filling system method
It is made mainly from inorganic minerals such as clay, calcium carbonate and gypsum, supplemented by lightweight materials (such as perlite), reinforcing fibers (such as pulp) and binders (such as water glass), through cold mixing, molding, drying and film curing.
?
Representative patent: Disposable biodegradable tableware and its manufacturing method.
?
Advantages: Wide sources of raw materials, low cost, and no reliance on food crops;
Disadvantage: The degradation mechanism is physical disintegration rather than complete biochemical decomposition, and the ecological impact needs further assessment.
?
5. Multi-component compound formula system (New and improved type
Combine starch, plant fiber, biodegradable polyester and other ingredients to improve the overall performance.
?
?
The use and disposal of biodegradable disposable tableware
Precautions for Use
Degradable tableware made of different materials has strict restrictions on temperature and food types:
?
Temperature control
The operating temperature of most degradable tableware should not exceed 100℃. For example:
The heat resistance of PLA material is only up to 100℃; beyond that, it is prone to deformation.
PBAT cannot be used in frozen food.
PHB should not come into contact with alcoholic foods.
?
Microwave heating
Not all tableware labeled as "degradable" can be heated in a microwave. PBT type can, but PLA is prone to melting and deformation under microwave.
?
Avoid reuse
Even if the quality is good, it should be discarded immediately after use. Especially after holding high-temperature or oily food, reusing it may release harmful substances.
?
Identify authenticity
Check whether the label indicates "food contact", implementation standards, manufacturers and materials;
If there is a pungent smell after opening the package, it may be made of inferior raw materials and should be stopped immediately.
?
Scientific disposal methods
Proper disposal is the key to achieving an environmental protection closed loop.
?
Garbage sorting and disposal:
It should be classified as kitchen waste or organic waste in order to enter the composting system.
It should not be mixed into the ordinary plastic recycling stream to avoid contaminating the quality of the recycled material.
?
Home composting applicability:
Starchy and pulp molded products can decompose relatively quickly in household composting.
PLA and other materials require industrial composting conditions (high temperature and high humidity), and their degradation is slow in a home environment.
?
Industrial composting priority:
In cities with the necessary facilities, biodegradable tableware should be sent to professional composting plants to be efficiently converted into organic fertilizers under controllable conditions.
?
Discarding is not recommended:
Although degradable, it still takes months or even longer to decompose naturally in soil or the ocean, and limited conditions (such as humidity and types of microorganisms) can affect the process.
?
Global future trends in biodegradable disposable tableware
With the increasingly serious problem of "white pollution", many countries and regions around the world have successively introduced plastic ban or plastic limit policies to promote the transformation of traditional plastic products to environmentally friendly alternatives.Biodegradable disposable tableware, which can be decomposed into harmless substances such as carbon dioxide and water by microorganisms in the natural environment, has become an important alternative in the fields of food and beverage take-out, retail and aviation catering.Under the influence of the three factors of environmental awareness, policy enforcement and technological progress, the industry is ushering in a window of rapid development.
?
1. Material diversification and technological upgrading
In the future, more non-grain crops such as bamboo pulp, bagasse and corn starch will be used to avoid land competition with food.At the same time, the development of waterproof and oil-proof but fluorine-free environmental protection coating technology, improve practicability.
?
2. Develop towards "sustainability + intelligence"
Packaging design tends to be lightweight and compostable.
Combined with smart tags (such as temperature sensing, traceability two-dimensional code), functional extension is realized.
?
3. Establishment of recycling and circular systems
Although "biodegradable," the best treatment still requires an industrial composting facility. In the future, international cooperation will enhance standard setting and promote the establishment of a unified recycling and degradation system.
?
?
Biodegradable disposable tableware is an important way to solve plastic pollution. Its core advantage lies in the recyclability of raw materials and the degradability at the end. However, the true environmental benefits still need to be supported by a corresponding classification and recycling system as well as an industrial composting system. Consumers should choose certified products, while enterprises can enhance their brand image and sustainable competitiveness through customized design. In the future, with technological advancements and cost reductions, this type of tableware is expected to become mainstream in the market.